Updated on December 2, 2024.
If you have high blood pressure, you may be on a treatment plan created by your healthcare provider (HCP) to help you lower your numbers. That may include modifying your diet and getting regular exercise.
But did you know that your sleep—or lack thereof—may be one of the root causes of your hypertension?
Understanding sleep apnea
If you experience excessive daytime sleepiness, concentration problems, dry mouth, choking sensations during sleep, and loud snoring, you may have sleep apnea. The most common type of sleep apnea is called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It occurs when the tissues and muscles at the back of the throat relax and collapse during sleep, causing the airway to become blocked.
People with OSA have repeated pauses in breathing while they sleep. These interruptions may range from a few seconds to a few minutes. They may occur as frequently as 30 or more times each hour.
Those pauses cut off oxygen to the brain and can raise blood pressure levels. Over time, they can lead to heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. Luckily, the treatments that help ease sleep apnea may reduce high blood pressure, too.
How sleep apnea treatments help hypertension
According to a 2022 review of research published in Current Hypertension Reports, treatments for OSA can often do double duty as treatments for high blood pressure when it’s caused by OSA.
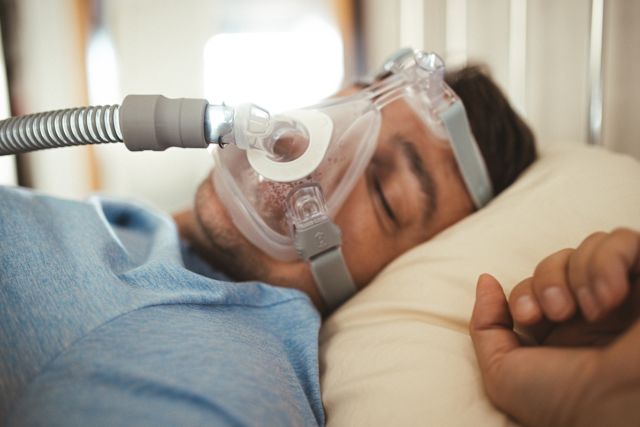
Researchers noted that continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), one of the primary treatments for OSA, is also effective at lowering high blood pressure related to OSA. A typical CPAP machine features a mouthpiece that the patient wears over their nose and sometimes mouth. A connected device provides a steady flow of air that helps keep the user’s airway open, preventing it from collapsing and blocking breathing.
Weight loss is also a common treatment for OSA, since overweight or obesity can also contribute to tissue in the back of the throat blocking airflow. In fact, the researchers noted that weight loss has been reported to be just as effective for treating the type of high blood pressure that comes from OSA.
Mandibular advancement devices (MADs) are another effective non-medical, non-invasive treatment. These are mouthpieces that pull the jaw forward to help keep the airway open during sleep. Because it can be difficult to adjust to CPAPs, MADs are considered a good alternative. (Some patients simply never get used to the noise the CPAP machine makes or the mask itself.) MADs can help with mild or moderate obstructive sleep apnea but may not be the best option for severe obstructive sleep apnea.
How to know if you have sleep apnea
Sleep apnea can have serious health consequences, which is why you should tell your HCP if you think you or a loved one has the condition. Look out for these warning signs:
- A rise in high blood pressure numbers
- Problems with memory or concentration
- Feeling tired when you wake up
- Exhaustion or falling asleep throughout the day
- Waking with sore throat or headache
- Frequent bed partner complaints about your snoring
Note, though, that while sleep apnea treatments may help control your high blood pressure, they may not be enough. Medication is often necessary. Discuss with your HCP the best way to treat your high blood pressure and your sleep apnea.