Updated on December 20, 2023
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that interferes with a person’s ability to perceive reality. Schizophrenia causes a person to experience delusions and hallucinations, as well as difficulties with thinking, emotions, and behavior. A person will have no control over these symptoms without treatment.
While there is no cure for schizophrenia, the condition can be managed with treatment. The medications used to treat schizophrenia are called neuroleptic medications. These are also known as antipsychotic medications because they are used to treat psychosis, a collection of symptoms that occur when a person has lost contact with reality.
Along with neuroleptic medications, therapy (such as cognitive behavioral therapy) and social support are important parts of a treatment plan.
Many people with schizophrenia take neuroleptic medications in the form of oral medications, which are taken daily. Oral medications can refer to pills or liquid medications.
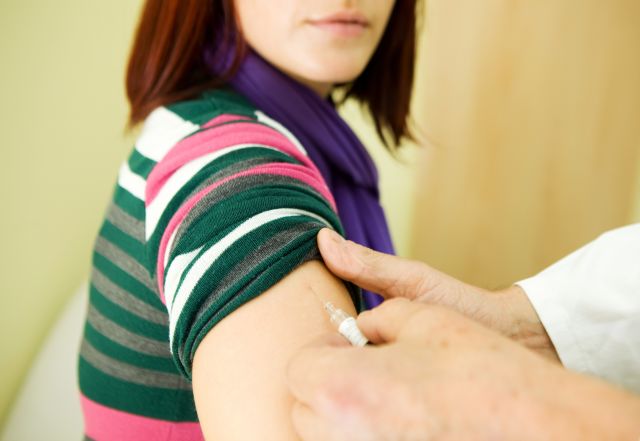
There are also long-acting injectable (LAI) neuroleptic medications, which are given as an injection administered by a healthcare provider.
How do LAI neuroleptic medications work?
LAI neuroleptic medications work the same way as oral neuroleptic medications. They contain drugs that act on specific neurotransmitters, chemicals that enable signaling and communication between nerve cells.
When a person has schizophrenia, neurotransmitters in the brain do not work normally, and blocking specific neurotransmitters helps control symptoms. (However, schizophrenia is a complex condition, and neurotransmitter dysfunction is only one aspect—also, the causes of schizophrenia are not fully understood).
When reading about LAI neuroleptic medications, you are likely to come across the terms “extended release” and/or “sustained release.” This refers to how long-acting medications are designed. The drug is suspended inside a substance that will be broken down slowly by the body, allowing the medication to be released at a steady rate over an extended period of time.
How often do you need to take an LAI?
This is an important question to discuss with your healthcare provider. The dosing schedule will depend on the specific medication being prescribed. Some medications need to be administered every other week, others require a monthly dose, and some are given once every few months.
Are LAI neuroleptic medications new?
Yes and no. Numerous LAI neuroleptic medications have been approved in recent decades, and new treatments for schizophrenia are always under development. But LAI neuroleptic medications have been in use since the 1960s.
Why might an LAI medication be recommended?
Treating schizophrenia with an LAI neuroleptic medication instead of an oral medication may improve adherence for some people. Adherence refers to taking a medication exactly as directed—or taking every dose on schedule. Nonadherence is common among people taking oral neuroleptic medications, and some studies have found that adherence improves when treating with an LAI.
However, treating and managing schizophrenia is a different experience for every person, and there are many reasons why a person and their healthcare providers might choose one medication over another. If you have questions, your healthcare provider will be your best source of information.