Updated on November 10, 2023
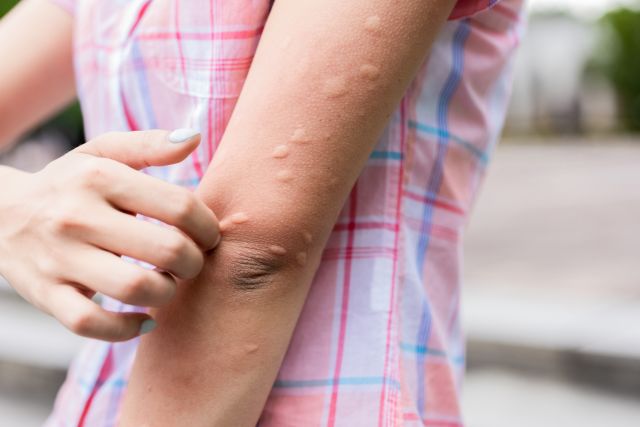
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)—formerly known as chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU)—is a condition characterized by hives and/or angioedema. Hives (or wheals) are inflamed itchy welts on the surface of the skin. Angioedema is inflammation in the deeper layers of the skin. Symptoms typically resolve within a day but recur frequently.
For a person to be diagnosed with CSU, these symptoms will occur on most days for a period of time lasting six weeks or longer. Diagnosis involves ruling out underlying conditions that may be causing the hives and checking for potential triggers that can induce symptoms (such as exposure to cold). With CSU, symptoms have no identifiable trigger.
Is CSU an autoimmune disorder?
The exact cause of CSU is not fully understood, but medical researchers have been able to learn a lot about what is happening in the body when a person has CSU. Research supports the idea that the immune system plays an important role, and that some cases of CSU are autoimmune disorders.
An autoimmune disorder is a condition where the immune system begins to malfunction and attack healthy tissues. In many cases, autoimmune attacks are associated with autoantibodies.
An autoantibody functions like an antibody. Antibodies bind to invasive substances (like infectious bacteria, viruses, or toxins) and mark them as targets for the immune system. Autoantibodies bind to specific proteins in healthy cells. This causes the immune system to target healthy cells.
What autoantibodies are related to CSU?
The type of autoantibodies that have been associated with CSU are called immunoglobulin E (IgE) autoantibodies and immunoglobin G (IgG) autoantibodies.
These autoantibodies interact with cells in the skin, causing a release of histamines. Histamines are chemicals that stimulate inflammation. The release of histamines in the skin results in hives, itching, and/or angioedema in CSU.
Autoantibodies are an important topic of research in CSU. Identifying the different autoantibodies involved helps medical researchers categorize CSU into different subtypes. This may lead to better tools to help diagnose and treat CSU.
While some cases of CSU have an autoimmune component, in many cases, the mechanisms that are causing CSU cannot be identified.
Are there tests for autoantibodies?
Testing for autoantibodies among people who have CSU is not commonly used. It is typically only performed alongside tests used to help diagnose thyroid disorders.
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that produces and releases hormones that regulate many functions throughout the body. Autoimmune hypothyroidism is one of several autoimmune disorders that can occur alongside CSU.
What autoimmune disorders are associated with CSU?
In addition to autoimmune disorders that affect the thyroid, several other autoimmune disorders are associated with CSU. Examples include:
- Vitiligo. The immune system destroys pigmentation in the skin, causing uneven patches of white skin with no pigmentation.
- Pernicious anemia. The immune system attacks a protein in the lining of the stomach, preventing the body from absorbing vitamin B12. Because the body needs B12 to make red blood cells, this leads to low numbers of red blood cells.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). An autoimmune disorder that can cause inflammation in many different parts of the body, including the joints, kidneys, skin, heart, lungs, brain, and blood vessels. Because it can attack many different parts of the body, SLE can cause a wide variety of symptoms.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA causes inflammation and damage to the tissues that make up the joints. Joint pain, stiffness (especially after rest), and fatigue are common symptoms.
Keep in mind that these are a few examples, and this is not a comprehensive list of the conditions that can occur alongside CSU. Also keep in mind that not every person who has CSU will have a co-existing autoimmune disorder.
However, the fact that other conditions occur alongside CSU reinforces the importance of working with a healthcare provider. Everyone’s health is different, and a treatment plan for CSU should be built around your health, your symptoms, and your needs.