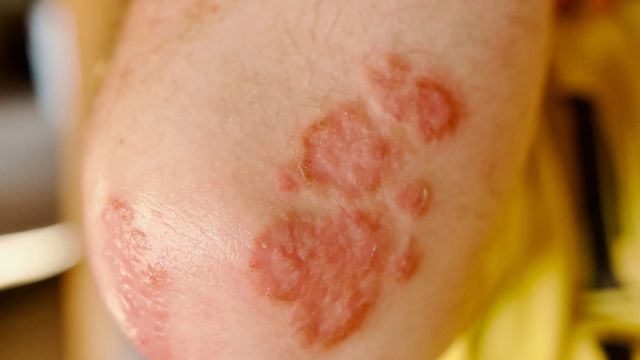
When thickened, itchy, red scaly patches erupt on your skin, all you’ll want is relief. And when you’re dealing with psoriasis, getting that relief starts with an accurate diagnosis.
That’s because five different types of psoriasis cause various symptoms that can mimic other skin diseases or even injuries:
- Plaque psoriasis affects some 80 to 90 percent of all people with psoriasis. The tell-tale plaques are red, symmetrical patches covered with silvery scales. These often appear on your scalp, knees, elbows, lower back, buttocks and arms, but the lesions can crop up anywhere—even inside your mouth. Outbreaks can be itchy or painful.
- Guttate psoriasis causes small, drop-shaped sores on your body, arms, legs or scalp. It’s most often triggered by infections, such as strep throat.
- Pustular psoriasis is marked by pus-filled blisters on top of swollen, red skin, most often on the palms and soles of your feet. Outbreaks are linked to medications, infections, stress or certain chemicals.
- Inverse psoriasis causes smooth, red patches in folds of skin near the genitals, under the breasts or in the armpits. Rubbing and sweating worsen inverse psoriasis.
- Erythodermic psoriasis results in red and scaly skin covering most of your body. Triggers include a bad sunburn or a reaction to certain meds, such as corticosteroids. Also, if you have psoriasis that’s not well controlled, it can escalate into EP. This a life threatening emergency. Seek immediate medical help or call 911.
Before recommending treatment, your healthcare provider will want to rule out other conditions, including atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, ringworm and pityriasis rosea, all of which are non-psoriasis skin conditions with psoriasis-like symptoms.
Psoriasis affects your whole body—not just the skin
Psoriasis isn’t just a rash—it’s an autoimmune disease. That means your body mistakes its own tissue as foreign and mounts an attack against itself. When you have psoriasis, your T-cells, a type of white blood cell, become overactive. They release chemicals that cause inflammation and trigger your skin to produce cells more quickly.
As a result, skin cells pile up on the surface of your skin in red, scaly patches.
Psoriasis can come and go and can flare back up when you’ve had an infection, are under stress or even when the weather dries out your skin. Certain medicines can cause flares, as can cuts, scratches and sunburn.
Getting an accurate diagnosis
Psoriasis also causes widespread inflammation within your body. As a result, you may have other conditions linked to inflammation, including cardiovascular problems, obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes and psoriatic arthritis, a condition that causes painful, swollen joints.
If there’s a question about whether your skin problem is psoriasis, your healthcare provider might take a small skin sample and examine it under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Treating psoriasis
As of yet, there is no cure for psoriasis. But there’s plenty of good news when it comes to treatment, because thanks to ongoing research, we now have many different and effective psoriasis treatments. Each one has benefits, drawbacks and possible side effects, say experts at the American Academy of Dermatology. Your dermatologist will work with you to find the best one for your needs.